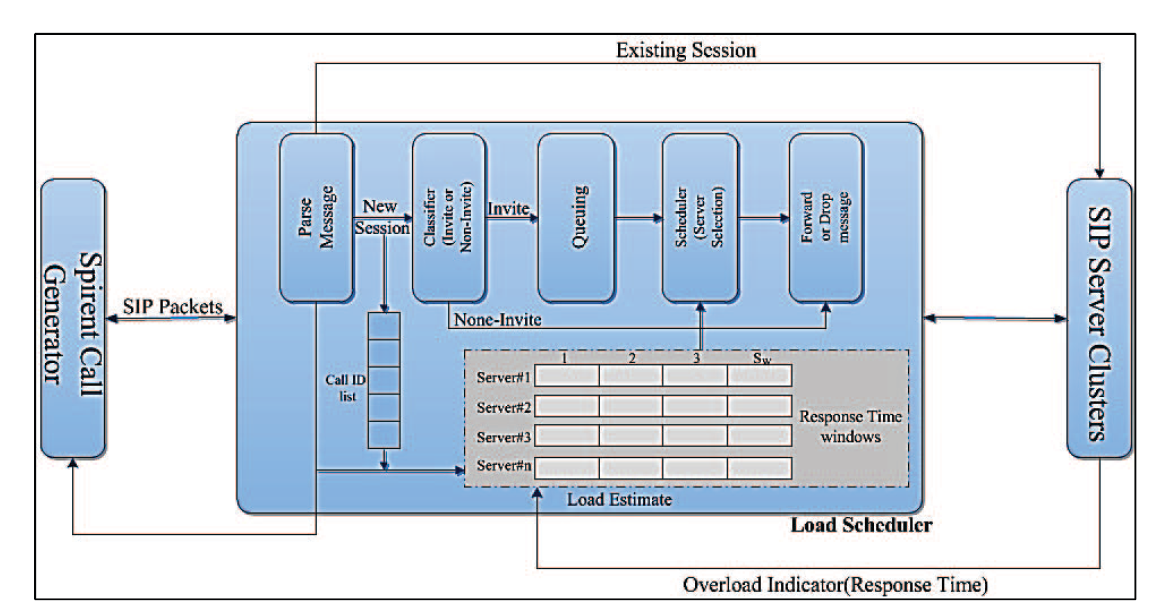
Widespread use of SIP as a signalling protocol in VoIP networks is the main reason for tackling various challenges. SIP throughput can severely be degraded when an overload situation happens in the proxy servers due to several retransmissions from user agents. In this paper we try to prevent throughput reduction by properly distributing the loads over available proxy servers. The proposed scheme utilizes response time of the servers as the main decision factor. The algorithm is implemented in a real environment using Spirent and Asterisk servers as call generator and load balancer respectively. The results of comparing the proposed method with some well-known algorithms indicate considerable throughput improvement up to 15% with a Round-Robin algorithm.